Skin conditions can be confusing, especially when they share similar symptoms like redness, irritation and discomfort. Two that are frequently mistaken for one another are psoriasis and eczema. While both cause visible changes to the skin, they have distinct causes and management approaches.
In this article, we look into the key differences between eczema vs psoriasis, how they present on different parts of the body and the steps involved when seeking a professional diagnosis or treatment options.
Definition and causes — psoriasis vs eczema
Eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis) is primarily an inflammatory skin condition often linked to allergic reactions, environmental triggers or genetic factors. The condition typically develops when the skin’s natural barrier becomes compromised, allowing irritants and allergens to penetrate more easily. This leads to inflammation, dryness and the characteristic itching that many individuals experience.
Psoriasis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This causes skin cells to multiply at an accelerated rate — up to 10 times faster than normal. As these excess cells build up on the skin’s surface, they form the thick, scaly patches that are characteristic of psoriasis.
Eczema vs psoriasis on the face
Facial presentations of these conditions can be particularly concerning for patients, as they’re highly visible.
Eczema on the face typically appears as red, dry patches that may weep or crust over. The skin often looks irritated and inflamed, with poorly defined borders. Common areas include the cheeks, around the eyes and near the mouth. Those affected may experience tightness, along with intense itching or a burning sensation. In adults, facial eczema often develops around stress points or areas frequently touched.
Psoriasis on the face presents as well-defined, raised red patches covered with silvery-white scales. These plaques have distinct, sharp borders and tend to be symmetrical. Facial psoriasis commonly affects the hairline, eyebrows, area between the nose and upper lip and around the ears. The scaling is typically more pronounced than with eczema, and the patches feel thicker to the touch.
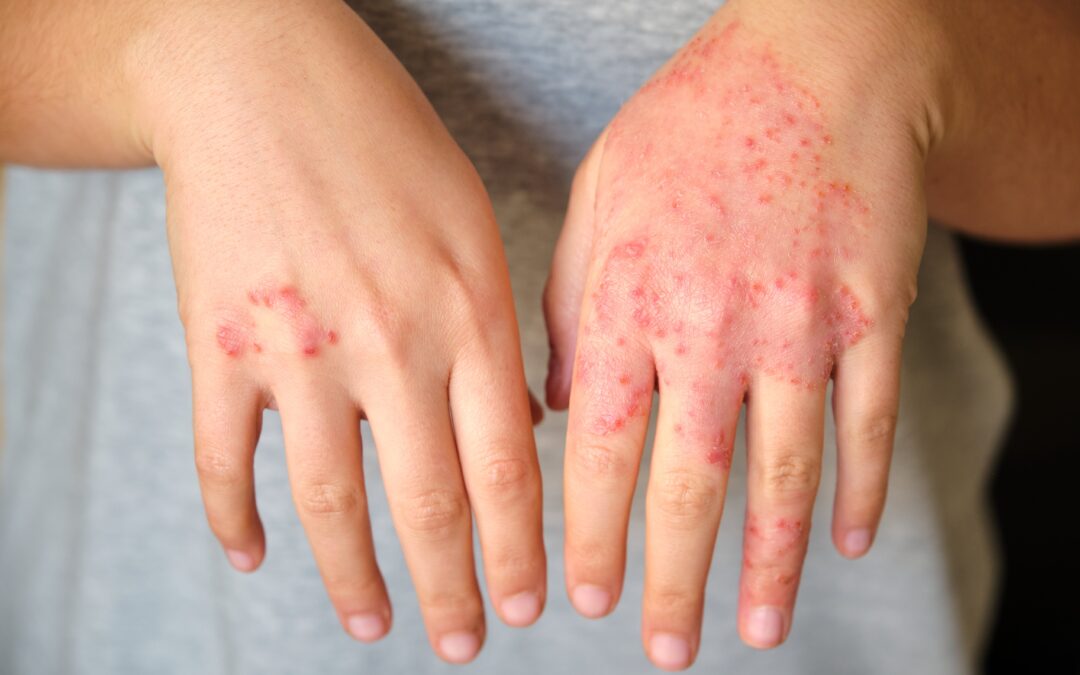
Eczema vs psoriasis on the hands
Hand dermatitis can significantly impact quality of life, making everyday tasks uncomfortable or painful.
Eczema on the hands often appears as small, fluid-filled blisters on the palms and sides of fingers, particularly in cases of dyshidrotic eczema. The skin may become extremely dry, cracked and painful. Contact dermatitis, another form of eczema, creates red, swollen areas where irritants or allergens have touched the skin. The inflammation is often widespread and may extend beyond the initial contact area.
Psoriasis on the hands typically manifests as thick, scaly plaques on the knuckles, back of the hands or palms. The affected areas have well-defined edges and may crack or bleed due to the thickness of the scales. Palm and sole psoriasis can be particularly challenging, creating deep fissures that are painful and slow to heal. The scaling pattern tends to be more localised and symmetrical compared to eczema.
Eczema vs psoriasis on the legs
Lower extremity involvement varies significantly between these two conditions.
Eczema on the legs commonly affects areas prone to dryness or friction, such as the shins, behind the knees and around the ankles. The appearance is often patchy and irregular, with areas of dry, scaly skin interspersed with inflamed regions. Venous eczema, which occurs due to poor circulation, typically appears on the lower legs and ankles as brown, discoloured patches that may become sore or develop into open wounds if not treated.
Psoriasis on the legs presents as clearly defined, raised plaques that are often symmetrical. The front of the shins is a common location, along with the knees and thighs. These plaques maintain their characteristic thick, silvery scales and defined borders. The lesions tend to be more stable in location and appearance compared to the variable nature of eczema patches.
Eczema vs psoriasis on the scalp
Scalp conditions can be challenging to differentiate due to hair coverage obscuring visual assessment.
Eczema of the scalp (seborrheic dermatitis) typically creates yellowish, greasy scales along with redness and itching. The scaling tends to be finer and more diffuse, often extending to areas like the eyebrows, nose creases and behind the ears. The hair itself usually remains unaffected, and hair loss is uncommon.
Scalp psoriasis produces thick, silvery-white scales that may extend beyond the hairline onto the forehead, back of the neck and around the ears. The plaques are well-defined and may cause temporary hair loss in severe cases, though permanent hair loss is rare. The scales in psoriasis are typically thicker and more adherent than those seen in seborrheic dermatitis.
How to diagnose psoriasis vs eczema
Accurately distinguishing between psoriasis and eczema requires evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional. Because the two conditions can appear similar, self-diagnosis may lead to ineffective treatment and delayed results. Your consultation will likely include:
- Initial clinical assessment — A doctor will begin with a thorough medical history, including family history of skin conditions, autoimmune diseases or allergies. They’ll examine the affected areas, noting the pattern, distribution and specific characteristics of the lesions.
- Physical examination techniques — Medical professionals use specific diagnostic techniques to differentiate between conditions. They may perform the “scratch test” — gently scraping scales to observe underlying skin characteristics — or press on the lesions to assess how the skin responds.
- Treatment planning — Once diagnosis is established, the medical team will develop an appropriate management plan. This may include prescription medications, lifestyle modifications or in-clinic therapies. Follow-up appointments allow for treatment adjustment and monitoring of response.
Book a consultation with Advantage Skin Clinic
Persistent or worsening skin symptoms shouldn’t be ignored. While some mild flare-ups can be managed with over-the-counter products, a formal assessment is key to understanding the underlying cause and preventing complications.
At Advantage Skin Clinic, our team of experienced doctors and registered nurses is skilled in assessing and managing chronic skin conditions, including psoriasis and eczema. We combine medical insight with access to advanced diagnostic tools to support your skin health.
If you’re unsure what’s behind your symptoms or haven’t found relief, we’re here to help. Get in touch with any questions, or book a consultation at our Wollongong skin clinic today.